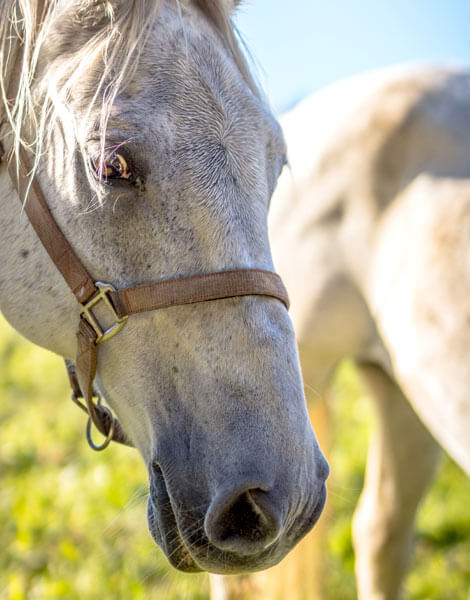
The whimsical color of horses
There is something whimsical about the breed of horses. Their colors specially. Horses have played a large role in contributing to the enhancement of civilization. Because of this, it has earned a lot of recognition and honor. When thinking of horses, great qualities and virtues come to mind such as: nobility, power, grace, strength, freedom and beauty comes to mind. Narrowing it down to the specifics, we will talk about the various graceful colors that they possess.
Horse coat colors are dependent upon genetics, just as our hair and eye colors are. Red, bay and black are the three base colors that horse colors stem from, but what are the most common colors? Keep reading to find out. Horses come in majorly base colours, the silver gene, Appaloosa patterns, White Patterns, and the champagne gene. The colours range from solid and static to multifaceted and ever-changing. These coat colors are controlled by complex genetics. Here, we showcase some common equine coat colors you might come across
LET’S BUILD SOMETHING GREAT. TOGETHER.
BASE COLORS
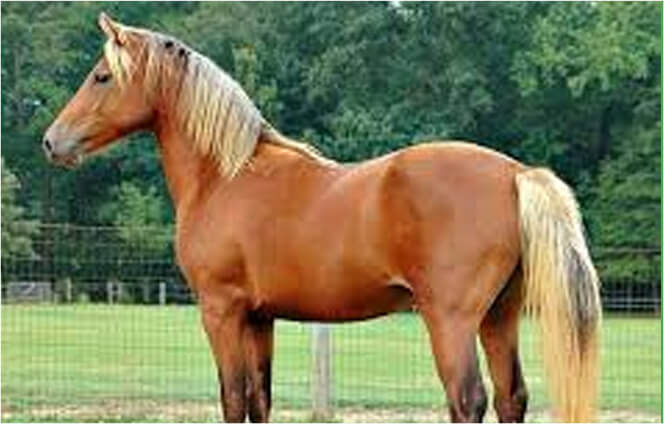
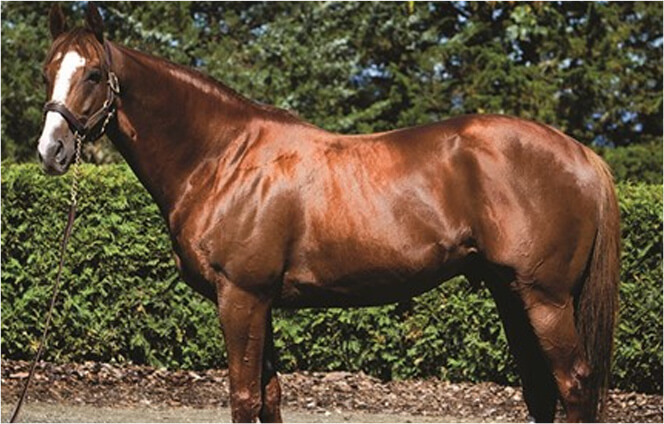
CHESTNUT
A chestnut is a red(ish) horse with no black pigment. Chestnuts vary greatly, from pale with a light mane and tail (flaxen), to a deep burgundy that can be mistaken for black. Although there is great variation in this color, most chestnut horses will fall into the middle of this color spectrum and are easy to recognize. A chestnut will never have black legs or a black mane and tail. They can however have a mane and tail that is darker than their body even to the point of being “almost” black
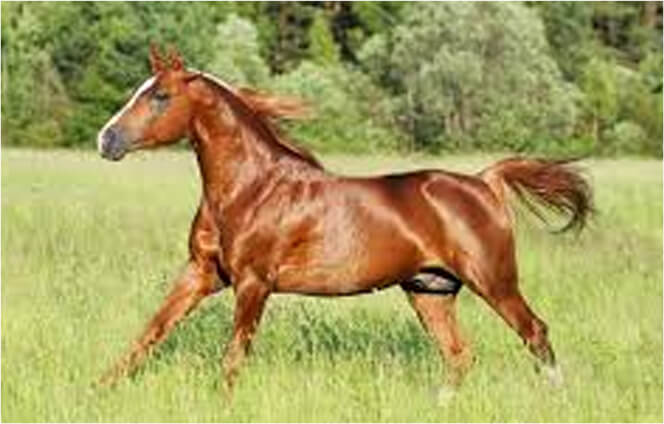

BAY
A bay is a red(ish) horse with a Black mane and tail and also black lower legs. They also have black "ear tips" meaning that the very tips of the ears will be black. The black areas of a bay horse are referred to as "points". The bay horse's body will be the same color as the chestnuts above and can vary to the same degree

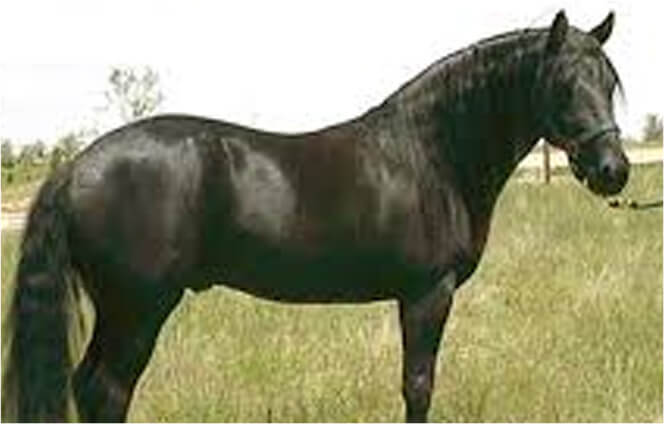
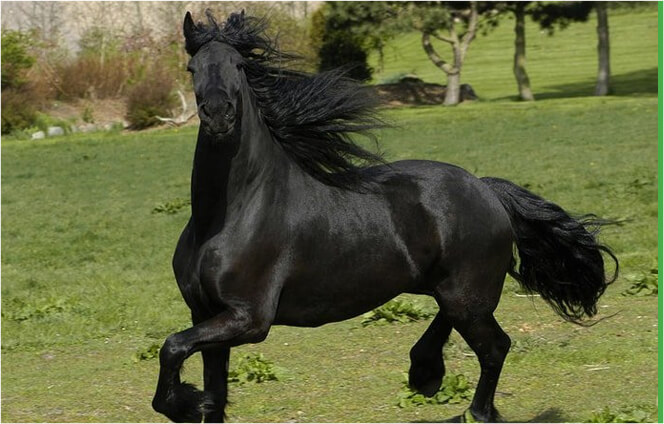
BLACK
A black horse is ideally solid black with no brown hair. Blacks can fade however and in some blacks this can result in a reddish tinge to the mane, end of the tail or coat. In some horses fading can be reversed by feeding minerals but some black horses will fade even when all nutritional needs are met. It is not known at this time why such fading occurs.


The Silver Gene
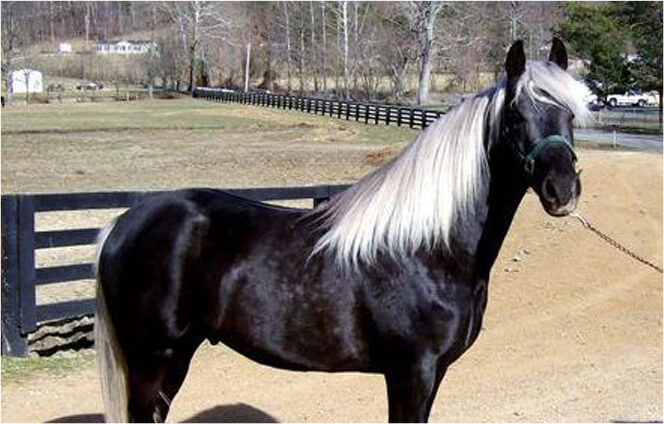
Black Silver
Silver in horses affects areas that would otherwise be black, changing the color from black to gray or brown. It has it’s greatest effect on a horse’s mane and tail. In horses that are heavily affected the mane and tail can be almost completely white or silver. If the horse also has feathers (the hairs on the horse's pastern), the feathers will be affected to the same extent as the mane and tail. Because silver only affects black pigment, Chestnut horses and the red body of Silver Bays will not be changed.

BAY Silver
Silver Dilution is a dominant trait, so in order to inherit the trait, a horse requires only one parent to carry and pass on the gene. Somewhat similar to the agouti gene, the silver dilution gene will only alter black pigmented horses (Ee or EE) and has no effect on red pigmented horses (ee). The agouti gene alters the coat by controlling distribution of the black pigment whereas the silver dilution gene does so by diluting areas of black pigment.

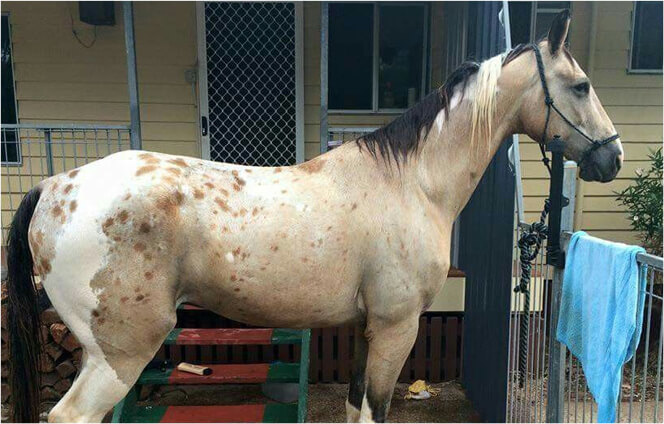
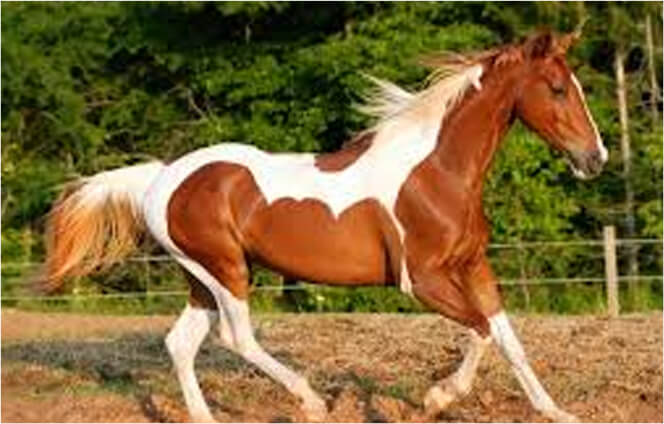
Appaloosa Patterns in Horses
Spots
White or dark spots.
A horse can be called spotted even if the spots are distributed over a certain portion of the body only.

Snowflake
When a dark body is adorned with white spots or flecks, it is commonly referred to as snowflakes. A snowflake appaloosa will often develop more and more spots and flecks as it grows older, and it is also normal for the size of the spots and flecks to increase.
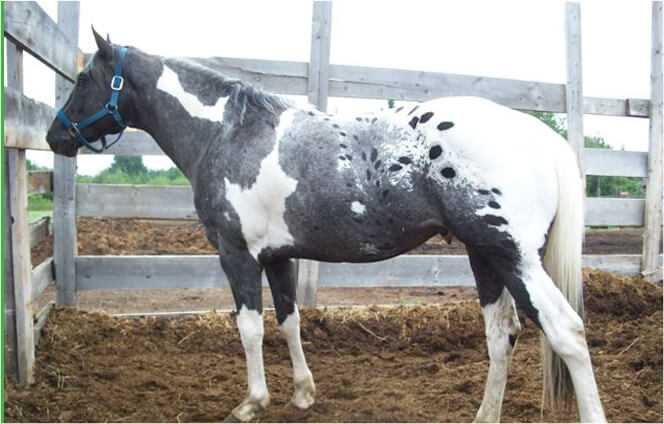
Leopard
A white horse with dark spots is called a leopard if the spots are distributed all over the body. If the horse is mostly white but with a bit of color remaining around the flank, neck and head, it is known as a few spot leopard.
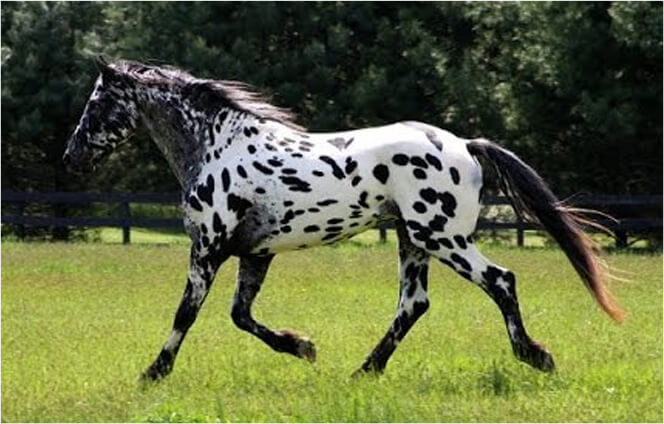

Black/Snowcap
A solid white covering the hip area, and contrasting against the base color of the horse, is known as a blanket or a snowcap. The white covering doesn’t have to be limited to the hip area; it can extend further.
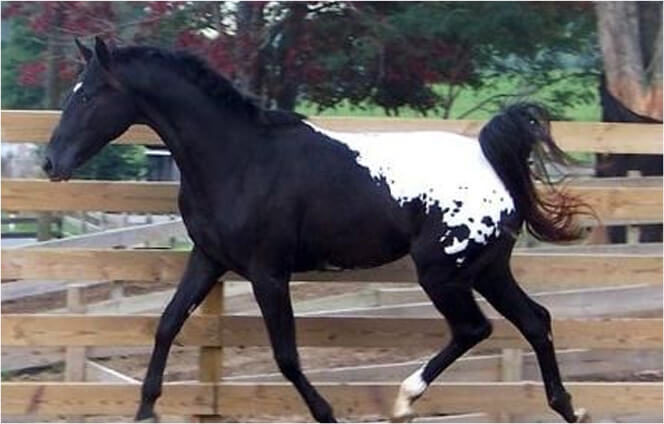

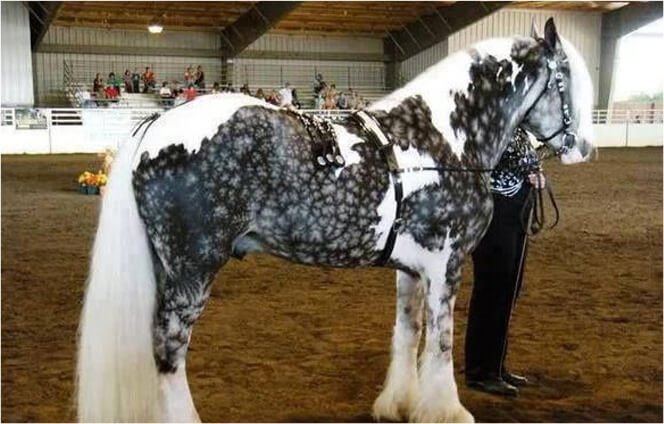
Varnish Roan
This is a distinct version of the leopard complex, and is characterized by:
- Intermixed dark and light hairs.
- A lighter color on the forehead, jowls and frontal bones of the face.
- A lighter color on the back, loin and hips.
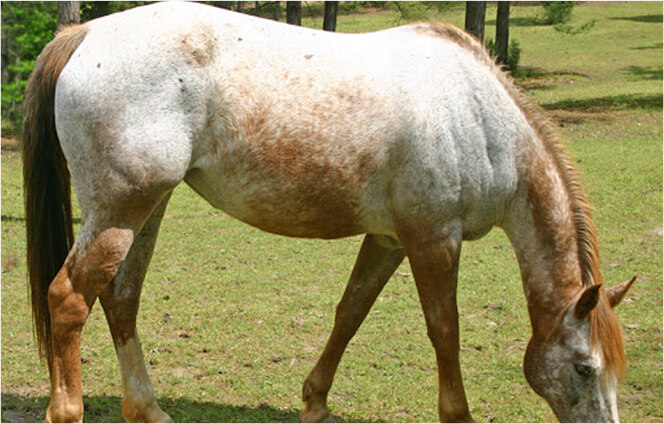

Frost
A solid white covering the hip area, and contrasting against the base color of the horse, is known as a blanket or a snowcap. The white covering doesn’t have to be limited to the hip area; it can extend further.

Pintaloosa
The Appaloosa has several distinctive colour patterns and all of the regular coat colours. Some Appaloosas have a solid colour except for a white patch over the hips, interspersed with small, round spots of the same colour as the body. Others have a basic solid colour with white dots over the entire body or are white with coloured dots